Managing risks is a critical component of Procurement Management and the Procurement Function.
Procurement Professionals are also responsible for ensuring a steady supply of Mission Critical Inputs that meet quality, price, and delivery criteria. The modern supply chain poses a growing number of risk factors that affect the modern business landscape. Protecting their organizations from risks is a critical part of the Procurement Function Mandate.
The following are ways that procurement professionals can effectively manage risks in their environments:
1.) Acquiring the necessary skills to effectively manage risks: Managing risks effectively is no light matter. Procurement professionals must be trained to scan their strategic and operational environments for risk factors. They must be able to competently spot, prioritize, and deploy risk mitigation methodologies. The goal will be to prevent supply chain disruption and business loss. Procurement leaders are responsible for ensuring that their teams have the required skills to deploy such methodologies.
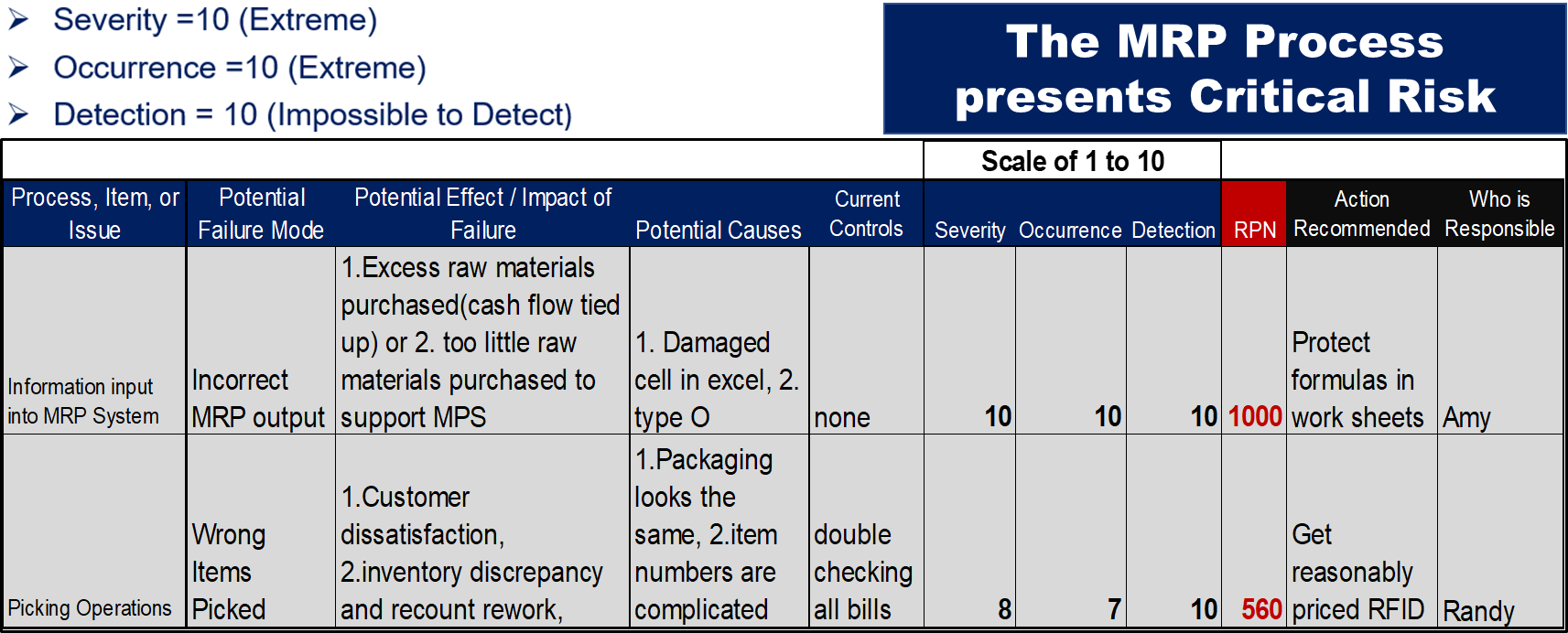
2.) Mastering a robust Risk Management Methodology such as FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a methodology that prioritizes. FMEA is underpinned by RPNs (Risk Priority Numbers) which rank risk factors by the degree of impact to key stakeholders they represent. The idea is that not all supply chain problems are equal, and procurement professionals must demonstrate a profound ability to identify, prioritize, and mitigate the risk factors they encounter. The formula for RPN is Occurrence times Severity times Detection, on a scale of 1 to 10.
Table 1, FMEA for MRP Process Permission for use granted by USA LEAN Engineering, LLC
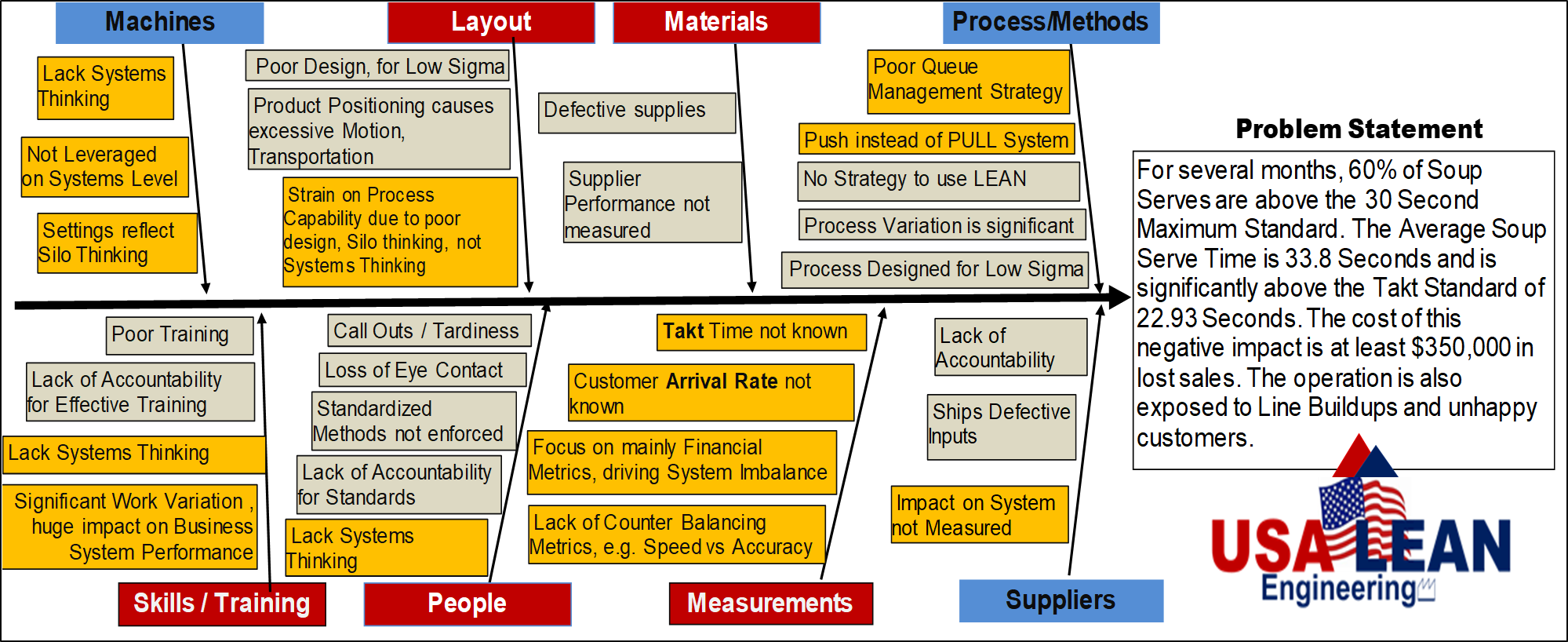
3.) Mitigating risks at the Root Cause Level: Understanding problems, failure modes and the risks they create at the root level is key to mitigate, prevent, and solving such issues. There are many methodologies for determining root causation. One such methodology is the fishbone diagram, where critical systems factors are analyzed for causes of non-conformance to specification and risk elements. The following is a fishbone diagram for a soup serve process.
Figure 2, Fishbone Diagram Permission for use granted by USA LEAN Engineering, LLC
The goal of the fishbone methodology is to probe for causation patterns from the systems factors. The systems factors are machines, people, materials, processes, measurements, and suppliers. From this exercise, procurement professionals can home in on the “Suppliers” systems factor.
4.) Quantification of risk factors to draw senior management attention: The effective quantification of risk factors in terms of dollars can surely draw the attention of key stakeholders and senior management, making a call to action more effective. The following is a chart that will clearly serve this purpose. The Pareto chart draws from the elements of the fishbone diagram but quantifies them in monetary terms.
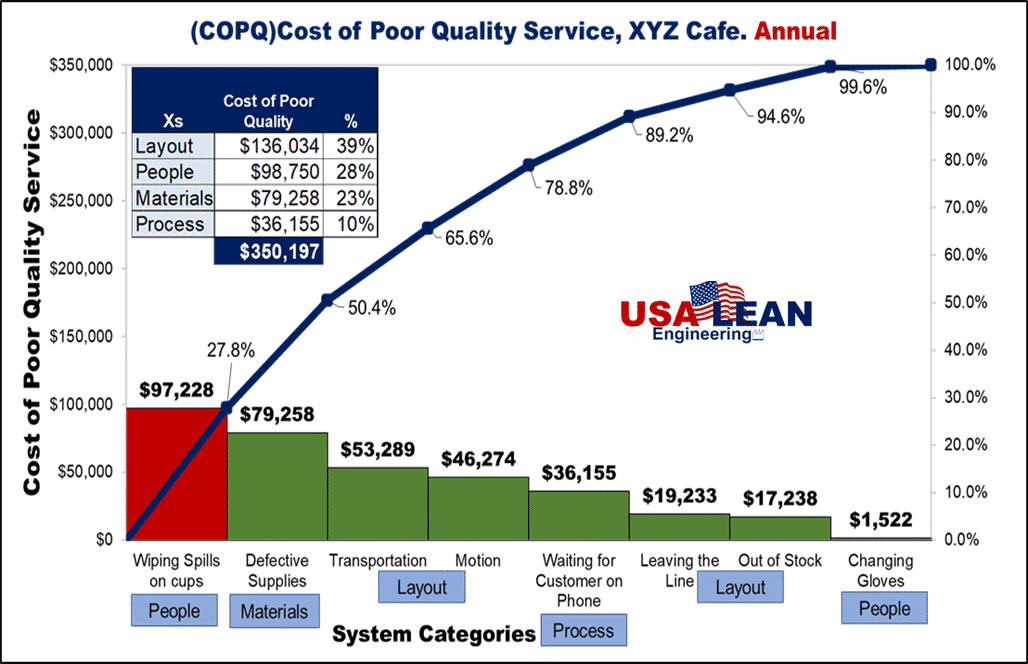
Figure 3, Pareto Chart Permission for use granted by USA LEAN Engineering, LLC
Note the fiscal impact of defective supplies from suppliers ($79,258 annually). Each of the system categories poses risks and must be dealt with in a manner that is cost-effective. The key is to determine the cost of risk mitigation relative to the fiscal impact of the risks themselves. A care cost-benefit analysis must be done to assure that risk mitigation strategies and tactics are cost-effective.
NLPA Learning: Looking for authoritative procurement templates, tools, webinars, and more? Stop trying to create resources from scratch and start taking advantage of having exactly what you need right at your fingertips in NLPA Learning.